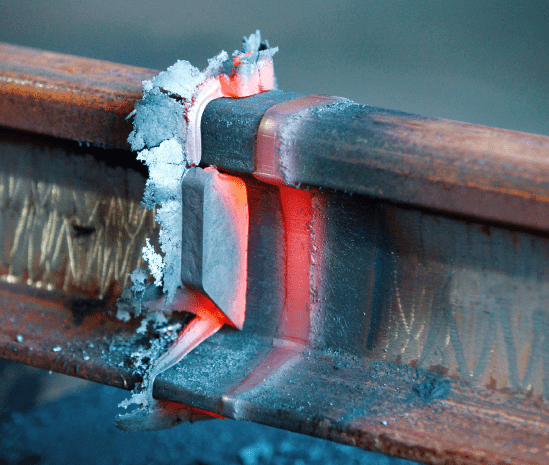
Flash welding is a popular resistance welding technique that involves joining two pieces of metal together using an electric arc. This technique is applicable for users in the metal-making industry.
It has become one of the popular methods for welding steel but also for nickel, aluminum, and titanium alloys. These metals are important for manufacturing sectors such as automotive, aerospace, heavy equipment, and more.
This blog post will go into detail on what flash welding is, the process of doing it, and why it's essential in the manufacturing industry.
Flash Welding Explained
Flash welding uses an electric arc to generate power. This actually conserves power when compared to alternative processes. An electric arc is struck between two parts of metal positioned close to one another. The heat from this arc melts the surfaces together, which causes them to form a bond almost instantly. Afterward, the electric current from the arc is removed and the metal parts cool before the welding force is removed. The resultant particles and other flash debris that is left on the surface of the metal parts are then mechanically removed. The weld interface is generally clean virgin material because all of the oxides and defects were expelled by the arcing action.
![Electrodes. (a) (c) (b) (d) Position and Clamp the Parts. Flash. The basic steps in a flash welding sequence are as follows: (1) Position the parts in the machine. (2) Clamp the parts in the dies (electrodes). (3) Apply the flashing voltage. (4) Start platen motion to cause flashing. (5) Flash the normal voltage. (6) Terminate flashing. (7) Upset the weld zone. (8) Unclamp the weldment. (9) Return the platen and unload. The above slide illustrates these basic steps. Additional steps such as preheat, dual voltage flashing, postheat, and trimming of the flash may be added as the application dictates. Upset and Terminate Current. Apply Flashing Voltage. and Start Platen Motion. [Reference: Welding Handbook, Volume 2, p.583, AWS]](/images/BasicStepsinFlashWelding.jpg)
Flash Welding Process
To perform flash welding, technicians will begin by clamping the ends of two pieces in electrode/clamps and hold the ends close to each other. The power is initiated and an arc is formed across the gap. Then the parts are brought together with force.
The arc continues to heat the two ends as they are pushed together to form a fused joint. During this process flash and expelled material is generated, which is why it is called “flash welding.” This continues for a brief period until a sound joint has been formed then the current is stopped.
Afterward, the welders will hold the two pieces together until the weld cools and solidifies. Excess flash must be removed and the weld inspected for any defects.
What Industries Is Flash Welding Used In?
Flash welding is applicable in a variety of industries. Below are some of the most common:
- Automotive Manufacturing
- Aerospace Manufacturing
- Heavy Equipment Manufacturing
For example, flash welding is useful in joining parts in manufacturing cars, trucks, and other vehicles. It's common in the assembly line process where several pieces form a larger component that will eventually be part of an entire vehicle. Flash welding is essential in assembling bumpers with fenders or doors with roofs. It also helps in the production of exhaust systems. Steel wheel rims for bicycles, cars, trucks, heavy equipment are all flash welded.
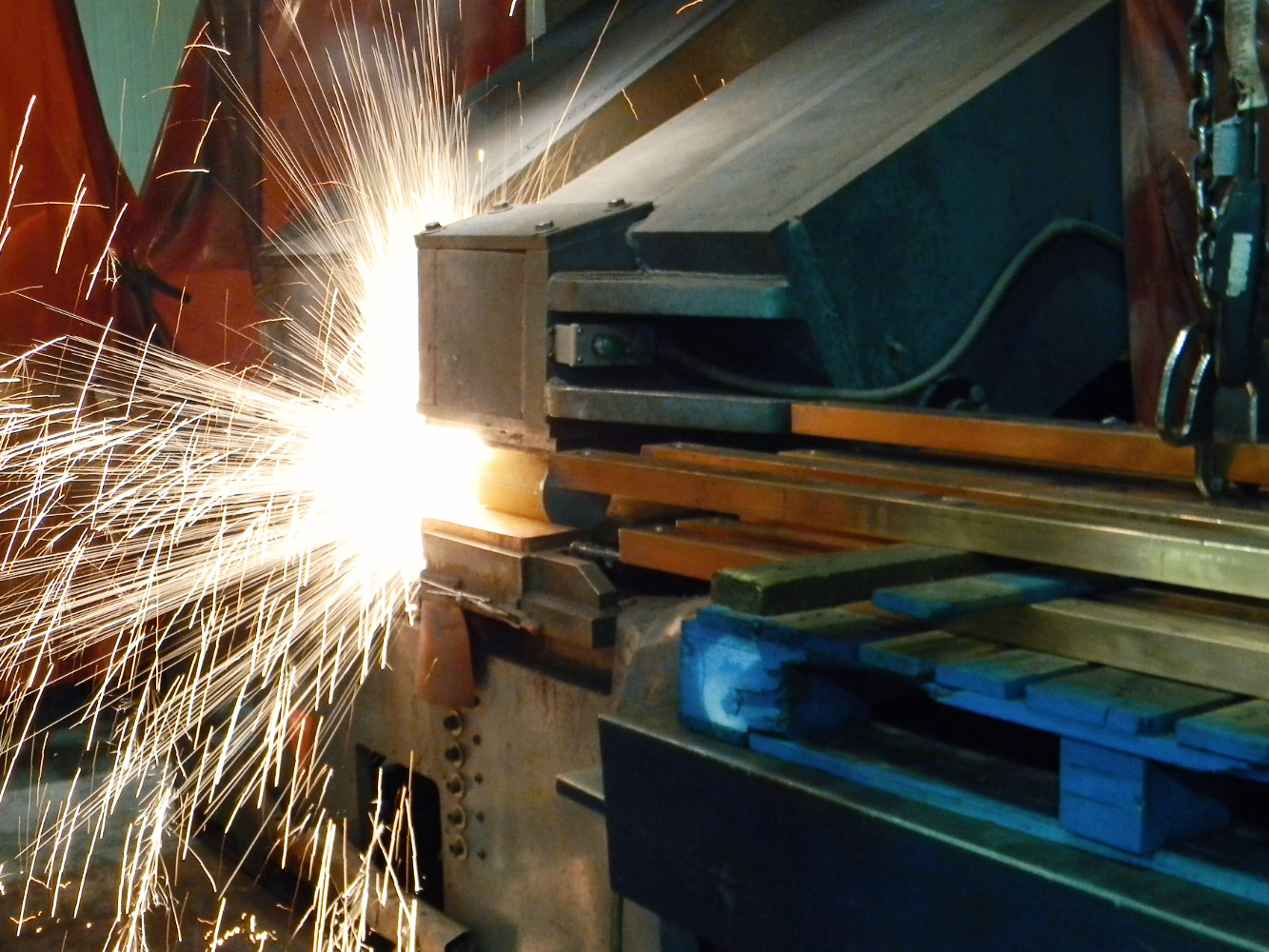

The Advantages Of Flash Welding
Below are some of the biggest advantages to flash welding:
1. It’s An Efficient Way to Join Various Metal Components Together
Flash welding gives welders the ability to put complex steel, aluminum, nickel, and titanium metals of various shapes and sizes together. Due to the unique complexities of these metals and shapes, other welding methods are not useful.
2. Generates High-Quality Products
Flash welding is a resistance welding technique that generates high-quality welds. The force of the weld allows contaminants to be squeezed out during the process. This means that welders can have an easier time connecting metal parts without worrying about solidification cracking and porosity, which are common defects in other welding techniques.
3. It Can Be Useful in a Variety of Applications
Flash welding is a versatile process applicable in a wide range of manufacturing operations. In addition to the automotive and aerospace industries, it's commonly used in the construction, metal fabrication, and shipbuilding industries.
Conclusion
Flash welding is a necessary process that offers several benefits for manufacturers. It's a fast and efficient way to combine metal components, and it generates high-quality products with few defects. Additionally, it’s suitable for use in various manufacturing applications and is relatively cheap to implement. For these reasons, flash welding is essential for any manufacturer looking to quickly produce the best metal products.
Be sure to keep up with our weekly blog as we tackle questions important to the manufacturing industry. You can find us on Linkedin, Twitter, and Facebook as well and be a part of the conversation! For business inquiries, contact us at tuffaloy.com.